Human Metapneumovirus (HMPV): Symptoms, Treatment, and Prevention
Updated on : 09 January, 2025
Image Source: herzindagi.info
What is HMPV? A Brief Overview
Image Source: assettype.com
Human Metapneumovirus (HMPV), identified in 2001, is a member of the Pneumoviridae family, which includes Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV). It primarily affects children, the elderly, and immunocompromised individuals, causing respiratory illnesses that range from mild cold-like symptoms to severe respiratory distress. HMPV spreads through respiratory droplets and can lead to serious complications in vulnerable populations.
The connection with COVID-19 is notable, as both viruses share similar transmission routes and symptoms, complicating diagnosis. However, HMPV generally has a lower mortality rate and lacks an available vaccine. As of January 2025, India has reported its first confirmed cases of HMPV, prompting increased surveillance and public awareness to manage respiratory illnesses effectively.
Global Trends of HMPV

Image Source: aljazeera.com
As of January 9, 2025, the Human Metapneumovirus (HMPV) has been increasingly recognized as a significant respiratory pathogen, particularly in the context of rising respiratory illnesses across various countries. Below is a summary of the current trends and case statistics globally.
Current Global Situation
-
China: There has been a notable surge in respiratory infections, including HMPV, particularly in northern provinces since December 2024. The Chinese CDC has reported increased cases among children under 14 years old. Although concerns have been raised about healthcare capacity, authorities have stated that hospitals are not overwhelmed and have not declared a state of emergency.
-
India: India has reported its first confirmed cases of HMPV, with ongoing monitoring by health authorities. As of January 6, 2025, there are seven confirmed cases across multiple states.
-
United States: The CDC has noted that HMPV typically follows seasonal patterns. Current data suggest that HMPV cases are increasing, but this aligns with expected seasonal trends for respiratory illnesses during winter months.
-
Europe: Reports indicate that HMPV is circulating in various European countries, although specific case numbers are less frequently reported. The European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC) is monitoring trends but has not identified unusual patterns compared to previous years.
Summary Table of Global HMPV Trends
| Country | Confirmed Cases | Notable Information |
|---|---|---|
| China | Increasing | Surge in cases, particularly among children; no emergency declared. |
| India | 7 | First confirmed cases; health authorities monitoring closely. |
| USA | Ongoing | Seasonal increase expected; health officials remain vigilant. |
| UK | Limited | Monitoring ongoing; no significant surge reported yet. |
| Europe | Variable | Cases circulating; ECDC monitoring trends without unusual patterns noted. |
Current Cases and Trends of HMPV in India

Image Source: abplive.com
As of January 9, 2025, India has confirmed a total of seven cases of Human Metapneumovirus (HMPV), marking the first instances of this virus in the country. The Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) has reported these cases across several states, with health officials maintaining that there is no significant cause for concern.
State-wise Breakdown of HMPV Cases in India
As of January 9, 2025, India has reported a total of eight confirmed cases of Human Metapneumovirus (HMPV). Below is a detailed table summarizing the cases by state:
| State | Confirmed Cases | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Karnataka | 2 | Two infants reported in Bengaluru: a three-month-old girl and an eight-month-old boy. |
| Maharashtra | 3 | Cases include a six-month-old girl in Mumbai and two previously suspected cases in Nagpur. |
| Gujarat | 1 | One case confirmed in Ahmedabad involving a two-month-old infant. |
| Tamil Nadu | 2 | Two cases reported, one each in Chennai and Salem. |
Symptoms and Public Health Response
Health officials are actively monitoring the situation, and the Union Health Ministry has advised the public to remain calm while encouraging hygiene practices to prevent further transmission.
The Discovery Journey: How HMPV Was Identified
The discovery of Human Metapneumovirus (HMPV) in 2001 marked a significant advancement in virology. Researchers from the Netherlands, led by Bernadette G. van den Hoogen, isolated the virus from the respiratory secretions of 28 young children experiencing respiratory infections. This was achieved using RNA arbitrarily primed PCR (RAP-PCR), a technique that allowed them to identify unknown viruses in cultured cells. HMPV was notable for its distinct characteristics, as previous testing methods had failed to identify it due to their focus on known respiratory pathogens like influenza and RSV. The identification of HMPV highlighted the necessity of recognizing lesser-known viruses contributing to respiratory diseases, prompting further research into its epidemiology and clinical implications.
Virology of HMPV
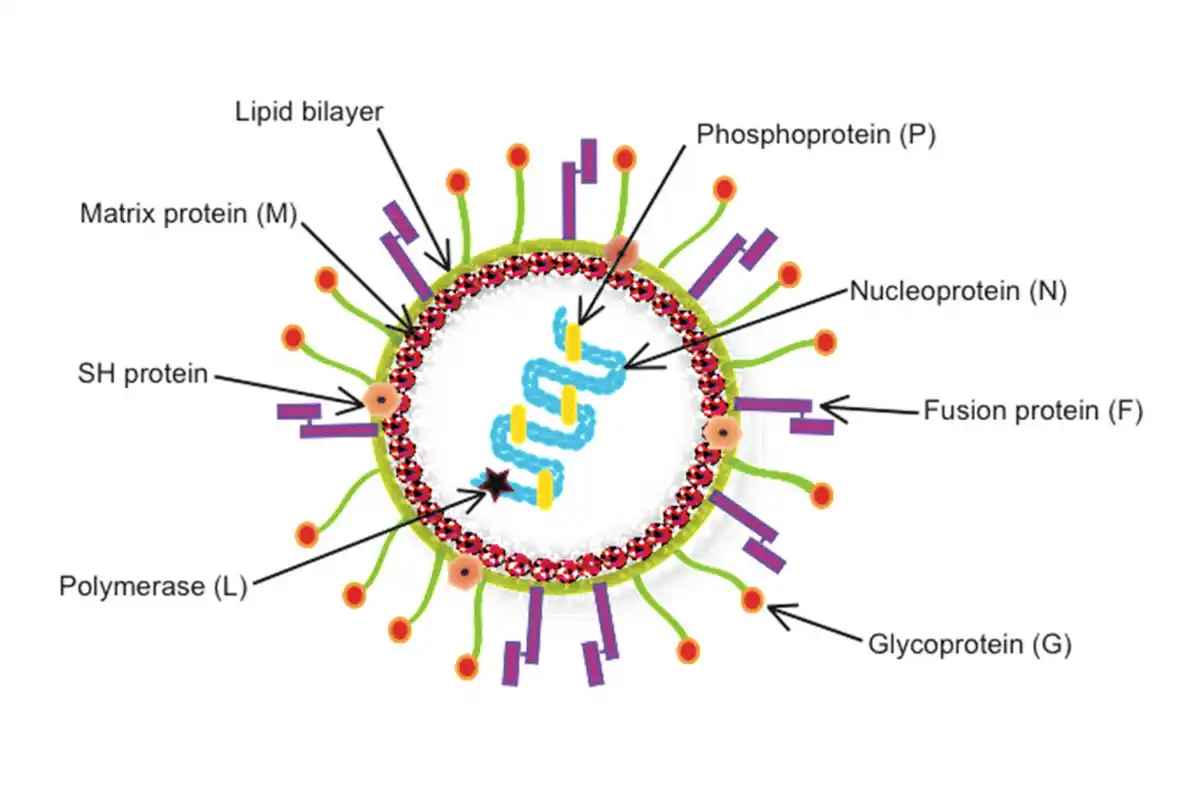
Image Source: wikimedia.org
Classification and Characteristics
Human Metapneumovirus (HMPV) is classified within the Pneumoviridae family, specifically under the Metapneumovirus genus. This family is characterized by enveloped viruses with non-segmented, negative-sense single-stranded RNA genomes. HMPV is divided into two main subtypes:
- Subtype A: Generally associated with more severe respiratory disease.
- Subtype B: Typically linked to milder infections.
Structure of HMPV
The structure of HMPV includes:
- An envelope derived from the host cell membrane.
- Surface glycoproteins, including the fusion (F) protein and glycoprotein (G), which are critical for the virus's entry into host cells.
- A single-stranded RNA genome that encodes several proteins necessary for viral replication and assembly.
Mechanisms of Infection
HMPV primarily infects respiratory epithelial cells through a multi-step process:
- Attachment: The virus binds to specific receptors on host cells via its G protein.
- Fusion: The F protein facilitates the fusion of the viral envelope with the host cell membrane, allowing viral RNA to enter the cytoplasm.
- Replication: Once inside, HMPV hijacks the host's cellular machinery to replicate its RNA genome and produce viral proteins.
- Assembly and Release: Newly formed virions are assembled and released from the host cell, ready to infect adjacent cells.
Epidemiology of HMPV
Global Reach: Where is HMPV Found?
Human Metapneumovirus (HMPV) has been detected worldwide, with reported cases across all continents. It is particularly prevalent in regions with temperate climates, though it has also been observed in tropical areas. Studies indicate that HMPV is a significant viral respiratory pathogen, contributing to acute respiratory infections in various populations globally, including children and the elderly.
Seasonal Trends: When Does HMPV Peak?
Epidemiological studies show that HMPV infections typically peak during the winter and early spring months. This seasonal pattern often coincides with the circulation of other respiratory viruses, such as Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) and influenza, leading to increased hospitalizations during these periods. In some regions, like northwest China, the peak occurs in September to October, while other areas may see peaks extending into late spring.
Who is Affected? At-Risk Populations
While anyone can contract HMPV, certain populations are at higher risk for severe disease:
- Infants: Particularly those under five years old.
- Elderly Individuals: Age-related decline in immune function increases susceptibility.
- Immunocompromised Patients: Individuals undergoing chemotherapy or those with chronic illnesses are more vulnerable.
- Individuals with Chronic Respiratory Conditions: Patients with asthma or Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) may experience exacerbated symptoms.
Popular Blogs
Symptoms and Clinical Manifestations of HMPV
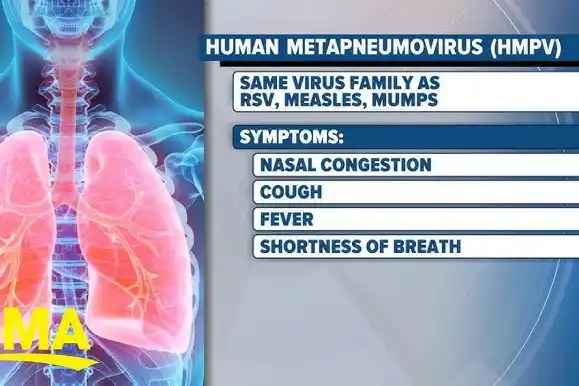
Image Source: ytimg.com
Recognizing the Signs: Common Symptoms of HMPV
Human Metapneumovirus (HMPV) infections can present a range of symptoms, which may vary from mild to severe. Common symptoms include:
- Cough
- Runny or stuffy nose
- Sore throat
- Fever
- Fatigue
Severe Cases: Complications and Risks
In vulnerable populations, particularly infants and older adults, HMPV can lead to serious complications, such as:
- Bronchiolitis
- Pneumonia
- Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS)
Differentiating HMPV: How it Compares to Other Respiratory Viruses
While symptoms of HMPV may overlap with those of other respiratory viruses like Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) and influenza, certain clinical features can help differentiate them:
- The severity of illness is generally higher in RSV compared to HMPV.
- The age distribution for severe cases often skews younger for RSV but includes both young children and older adults for HMPV.
Transmission of HMPV

Image Source: riversideonline.com
How HMPV Spreads: Modes of Transmission
Human Metapneumovirus (HMPV) primarily spreads through several key mechanisms:
- Respiratory Droplets: The virus is released into the air when an infected person coughs or sneezes, allowing it to be inhaled by others nearby.
- Direct Contact: Transmission can occur through physical contact, such as touching or shaking hands with an infected individual. If respiratory secretions are present on surfaces, touching these contaminated surfaces followed by touching one’s face can also facilitate infection.
- Contaminated Surfaces: HMPV can survive on surfaces for several hours, increasing the risk of indirect transmission, especially in crowded environments.
Understanding Risk Factors: Who is Most Vulnerable?
Certain factors heighten the susceptibility to contracting HMPV:
- Close Contact with Infected Individuals: Proximity to someone who is infected significantly increases the risk of transmission.
- Crowded Environments: Settings such as daycare centers, nursing homes, and hospitals are conducive to the spread of HMPV due to the close quarters and high interaction among individuals.
- Poor Hygiene Practices: Lack of proper hygiene measures, such as inadequate handwashing or not wearing masks during outbreaks, can enhance transmission rates.
Diagnosis of HMPV
Testing for HMPV: Methods and Procedures
The diagnosis of Human Metapneumovirus (HMPV) typically involves a combination of clinical evaluation and laboratory testing. Key methods include:
- Clinical Evaluation: Initial assessment is based on symptoms and patient history, focusing on respiratory illness presentations.
- Laboratory Tests: The most reliable diagnostic method is the Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) assay, which detects viral RNA from respiratory samples, such as nasopharyngeal swabs.
- Types of PCR: Commonly used techniques include:
- Multiplex Reverse Transcriptase-PCR (RT-PCR): This method allows for the simultaneous detection of multiple respiratory viruses, including HMPV.
- Real-Time RT-PCR: Provides quantitative results and is sensitive for detecting both lineages A and B of HMPV.
- Types of PCR: Commonly used techniques include:
- Rapid Diagnostic Tests: Although promising rapid tests are under development, they are not yet widely available in clinical practice.
Differential Diagnosis: Distinguishing HMPV from Other Infections
When diagnosing HMPV, healthcare providers must differentiate it from other respiratory pathogens. Important considerations include:
- Influenza Virus
- Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV)
- Adenoviruses
Treatment and Management of HMPV
Current Treatment Options: What Works?
Currently, there are no specific antiviral treatments approved for Human Metapneumovirus (HMPV); management primarily focuses on supportive care aimed at alleviating symptoms. Key supportive measures include:
- Hydration: Ensuring adequate fluid intake to prevent dehydration.
- Antipyretics: Over-the-counter medications like acetaminophen or ibuprofen can help manage fever and pain.
- Bronchodilators: These may be used for patients experiencing wheezing or significant breathing difficulties. In severe cases requiring hospitalization, additional interventions may include oxygen therapy or mechanical ventilation to support respiratory function.
Supportive Care Strategies for Patients
Supportive care is crucial in managing HMPV symptoms effectively:
- Fluid Intake: Maintaining adequate hydration is essential for recovery.
- Humidifiers: Using humidifiers can help ease breathing difficulties by adding moisture to the air.
- Monitoring: Patients should be closely monitored for any signs of deterioration that may necessitate advanced medical intervention.
Exploring Antiviral Research: What’s on the Horizon?
Research into antiviral therapies targeting HMPV is ongoing, with several promising candidates being evaluated:
- Ribavirin: This antiviral has shown activity against HMPV in vitro and has been used in some cases with immunocompromised patients, often in combination with intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG). However, its efficacy remains under investigation, and clinical trials are necessary to determine its safety and effectiveness.
- NMSO3: A sulfated sialyl lipid that has demonstrated potent antiviral activity against HMPV in animal models, showing promise for future therapeutic applications.
- Monoclonal Antibodies: Research is also being conducted on monoclonal antibodies targeting conserved epitopes of the HMPV fusion protein, which may offer prophylactic and therapeutic benefits.
Prevention Strategies for HMPV

Image Source: istockphoto.com
Effective Hygiene Practices to Reduce Spread
Preventive measures are crucial for controlling the spread of Human Metapneumovirus (HMPV) and can significantly lower infection risks. Key hygiene practices include:
- Regular Handwashing: Wash hands frequently with soap and water for at least 20 seconds, or use alcohol-based hand sanitizers when soap is not available. This helps eliminate the virus from hands after touching potentially contaminated surfaces.
- Avoid Close Contact: Limit interactions with individuals showing symptoms of respiratory illness to reduce the risk of transmission.
- Respiratory Etiquette: Cover coughs and sneezes with tissues or the elbow to minimize droplet spread, protecting both oneself and others.
- Surface Cleaning: Regularly disinfect frequently-touched surfaces and objects, such as doorknobs and shared toys, to reduce the risk of indirect transmission.
The Future of Vaccination: Research and Development Efforts
Vaccination against HMPV remains a priority in public health research. Several vaccine candidates are currently under investigation; however, none are yet available for public use. Developing an effective vaccine could significantly reduce the morbidity associated with HMPV infections. Ongoing research focuses on various approaches, including live attenuated vaccines and subunit vaccines targeting specific viral proteins.
HMPV in Relation to COVID-19
Image Source: etimg.com
As of January 9, 2025, Human Metapneumovirus (HMPV) has garnered attention due to its similarities and differences with COVID-19, especially in light of recent outbreaks in various countries. Understanding these aspects is crucial for public health responses and individual awareness.
Similarities Between HMPV and COVID-19
-
Respiratory Symptoms: Both HMPV and COVID-19 can cause respiratory illnesses, presenting symptoms such as fever, cough, nasal congestion, and shortness of breath. Vulnerable populations, including young children, older adults, and immunocompromised individuals, are at higher risk for severe illness from both viruses.
-
Transmission Modes: Both viruses are primarily transmitted through respiratory droplets from coughing or sneezing and can spread via contact with contaminated surfaces.
-
Seasonality: HMPV typically exhibits seasonal patterns, peaking during late winter to early spring, while COVID-19 has shown year-round transmission influenced by emerging variants and public health measures.
Differences Between HMPV and COVID-19
-
Severity of Illness: While both viruses can lead to respiratory symptoms, HMPV generally causes milder cold-like symptoms that may escalate to bronchiolitis or pneumonia in high-risk groups. In contrast, COVID-19 can lead to severe complications, including systemic symptoms like loss of taste and smell, multi-organ failure, and a broader range of complications.
-
Transmission Rate: HMPV is considered less transmissible than COVID-19. The mortality rate associated with HMPV is also lower compared to that of COVID-19, which has resulted in a global pandemic with significant morbidity and mortality.
-
Management Approaches: COVID-19 has benefited from the development of vaccines and antiviral therapies aimed at reducing severity and transmission. In contrast, management of HMPV primarily focuses on supportive care to relieve symptoms since no specific antiviral treatments or vaccines are currently available for HMPV.
Public Health Implications
The emergence of HMPV cases amidst the ongoing management of COVID-19 raises important considerations for public health authorities:
-
Monitoring: Increased surveillance for respiratory illnesses is essential to differentiate between HMPV and other respiratory viruses like influenza and RSV.
-
Preventive Measures: Standard preventive measures such as hand hygiene, mask-wearing, and social distancing remain effective in reducing the transmission of both viruses.
Future Directions in HMPV Research
Ongoing Research Initiatives: What We’re Learning
Current research initiatives are focused on various aspects of Human Metapneumovirus (HMPV) biology, which include:
- Subtype Impact: Investigating how different subtypes of HMPV affect disease severity and clinical outcomes.
- Host Immune Responses: Studying the immune responses elicited by HMPV infections to inform vaccine development strategies.
- Global Collaboration: Enhanced collaboration among researchers worldwide is facilitating knowledge sharing and improving management strategies for HMPV.
The Quest for a Vaccine: Promising Developments
The search for an effective vaccine against HMPV is ongoing, with several promising developments:
- Vaccine Platforms: Researchers are exploring various vaccine platforms, including live attenuated vaccines, subunit vaccines, and mRNA-based approaches similar to those used in COVID-19 vaccines.
- Antibody Research: Recent studies have identified antibodies that neutralize HMPV by targeting regions of the virus exposed before it enters host cells. These antibodies have shown protective effects in animal models.
- Structure-Based Design: Innovative approaches, such as structure-based design, are being utilized to inform vaccine development by identifying vulnerabilities in the viral proteins. This method has been successfully applied in the development of COVID-19 vaccines and is now being adapted for HMPV.
For instance, a team led by researchers at The University of Texas at Austin has made significant strides in understanding HMPV's structure and identifying neutralizing antibodies, which could pave the way for future vaccine candidates. Their work emphasizes the importance of detailed molecular insights in designing effective vaccines and therapeutics against HMPV.
Conclusion
Key Takeaways on HMPV
Human Metapneumovirus (HMPV) poses significant health risks across various populations, making understanding its characteristics essential for effective outbreak management. Key points include:
- Awareness of Symptoms: Recognizing symptoms such as cough, fever, and nasal congestion aids in early diagnosis, leading to better outcomes. In vulnerable groups, such as infants and the elderly, timely intervention can prevent severe complications.
- Preventive Measures: Implementing hygiene practices, including regular handwashing and avoiding close contact with infected individuals, plays a crucial role in reducing transmission rates, particularly during peak seasons in late winter and early spring.
- Research and Development: Continued research efforts are vital for developing effective treatments and vaccines against HMPV. Current studies focus on understanding the virus's biology, immune responses, and potential vaccine candidates.
The Importance of Continued Awareness and Research
As awareness grows regarding HMPV's implications for public health, ongoing research will be critical for developing effective management strategies moving forward. Key initiatives include:
- Public Health Campaigns: Focusing on hygiene practices can help mitigate outbreaks and educate communities about the risks associated with HMPV.
- Investment in Research: Funding and support for research into antiviral therapies and vaccine development will pave the way towards innovative solutions that could significantly reduce morbidity associated with HMPV globally.